例 6.16. 构造路径名
>>> import os
>>> os.path.join("c:\\music\\ap\\", "mahadeva.mp3") 
 'c:\\music\\ap\\mahadeva.mp3'
>>> os.path.join("c:\\music\\ap", "mahadeva.mp3")
'c:\\music\\ap\\mahadeva.mp3'
>>> os.path.join("c:\\music\\ap", "mahadeva.mp3")  'c:\\music\\ap\\mahadeva.mp3'
>>> os.path.expanduser("~")
'c:\\music\\ap\\mahadeva.mp3'
>>> os.path.expanduser("~")  'c:\\Documents and Settings\\mpilgrim\\My Documents'
>>> os.path.join(os.path.expanduser("~"), "Python")
'c:\\Documents and Settings\\mpilgrim\\My Documents'
>>> os.path.join(os.path.expanduser("~"), "Python")  'c:\\Documents and Settings\\mpilgrim\\My Documents\\Python'
'c:\\Documents and Settings\\mpilgrim\\My Documents\\Python'
|
os.path 是一个模块的引用;使用哪一个模块要看你正运行在哪种平台上。就像 getpass 通过将 getpass 设置为一个与平台相关的函数从而封装了平台之间的不同。os 通过设置 path 封装不同的相关平台模块。
|
|
os.path 的 join 函数把一个或多个部分路径名连接成一个路径名。在这个简单的例子中,它只是将字符串进行连接。(请注意在 Windows 下处理路径名是一个麻烦的事,因为反斜线字符必须被转义。)
|

|
在这个几乎没有价值的例子中,在将路径名加到文件名上之前,join 将在路径名后添加额外的反斜线。当发现这一点时我高兴极了,因为当用一种新的语言创建我自已的工具包时,addSlashIfNecessary 总是我必须要写的那些愚蠢的小函数之一。在 Python 中不要 写这样的愚蠢的小函数,聪明的人已经为你考虑到了。
|

|
expanduser 将对使用 ~ 来表示当前用户根目录的路径名进行扩展。在任何平台上,只要用户拥有一个根目录,它就会有效,像 Windows、UNIX 和 Mac OS X,但在 Mac OS 上无效。
|

|
将这些技术组合在一起,你可以容易地为在用户根目录下的目录和文件构造出路径名。 |
例 6.17. 分割路径名
>>> os.path.split("c:\\music\\ap\\mahadeva.mp3")  ('c:\\music\\ap', 'mahadeva.mp3')
>>> (filepath, filename) = os.path.split("c:\\music\\ap\\mahadeva.mp3")
('c:\\music\\ap', 'mahadeva.mp3')
>>> (filepath, filename) = os.path.split("c:\\music\\ap\\mahadeva.mp3")  >>> filepath
>>> filepath  'c:\\music\\ap'
>>> filename
'c:\\music\\ap'
>>> filename  'mahadeva.mp3'
>>> (shortname, extension) = os.path.splitext(filename)
'mahadeva.mp3'
>>> (shortname, extension) = os.path.splitext(filename)  >>> shortname
'mahadeva'
>>> extension
'.mp3'
>>> shortname
'mahadeva'
>>> extension
'.mp3'
|
split 函数对一个全路径名进行分割,返回一个包含路径和文件名的 tuple。还记得我说过你可以使用多变量赋值从一个函数返回多个值吗?对,split 就是这样一个函数。
|
|
我们将 split 函数的返回值赋值给一个两个变量的 tuple。每个变量接收到返回 tuple 相对应的元素值。
|

|
第一个变量,filepath,接收到从 split 返回 tuple 的第一个元素的值,文件路径。
|

|
第二个变量,filename,接收到从 split 返回 tuple 的第二个元素的值,文件名。
|

|
os.path 也包含了一个 splitext 函数,可以用来对文件名进行分割,并且返回一个包含了文件名和文件扩展名的 tuple。我们使用相同的技术来将它们赋值给独立的变量。
|
例 6.18. 列出目录
>>> os.listdir("c:\\music\\_singles\\")  ['a_time_long_forgotten_con.mp3', 'hellraiser.mp3',
'kairo.mp3', 'long_way_home1.mp3', 'sidewinder.mp3',
'spinning.mp3']
>>> dirname = "c:\\"
>>> os.listdir(dirname)
['a_time_long_forgotten_con.mp3', 'hellraiser.mp3',
'kairo.mp3', 'long_way_home1.mp3', 'sidewinder.mp3',
'spinning.mp3']
>>> dirname = "c:\\"
>>> os.listdir(dirname)  ['AUTOEXEC.BAT', 'boot.ini', 'CONFIG.SYS', 'cygwin',
'docbook', 'Documents and Settings', 'Incoming', 'Inetpub', 'IO.SYS',
'MSDOS.SYS', 'Music', 'NTDETECT.COM', 'ntldr', 'pagefile.sys',
'Program Files', 'Python20', 'RECYCLER',
'System Volume Information', 'TEMP', 'WINNT']
>>> [f for f in os.listdir(dirname)
... if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(dirname, f))]
['AUTOEXEC.BAT', 'boot.ini', 'CONFIG.SYS', 'cygwin',
'docbook', 'Documents and Settings', 'Incoming', 'Inetpub', 'IO.SYS',
'MSDOS.SYS', 'Music', 'NTDETECT.COM', 'ntldr', 'pagefile.sys',
'Program Files', 'Python20', 'RECYCLER',
'System Volume Information', 'TEMP', 'WINNT']
>>> [f for f in os.listdir(dirname)
... if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(dirname, f))]  ['AUTOEXEC.BAT', 'boot.ini', 'CONFIG.SYS', 'IO.SYS', 'MSDOS.SYS',
'NTDETECT.COM', 'ntldr', 'pagefile.sys']
>>> [f for f in os.listdir(dirname)
... if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(dirname, f))]
['AUTOEXEC.BAT', 'boot.ini', 'CONFIG.SYS', 'IO.SYS', 'MSDOS.SYS',
'NTDETECT.COM', 'ntldr', 'pagefile.sys']
>>> [f for f in os.listdir(dirname)
... if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(dirname, f))]  ['cygwin', 'docbook', 'Documents and Settings', 'Incoming',
'Inetpub', 'Music', 'Program Files', 'Python20', 'RECYCLER',
'System Volume Information', 'TEMP', 'WINNT']
['cygwin', 'docbook', 'Documents and Settings', 'Incoming',
'Inetpub', 'Music', 'Program Files', 'Python20', 'RECYCLER',
'System Volume Information', 'TEMP', 'WINNT']
|
listdir 函数接收一个路径名,并返回那个目录的内容的 list。
|
|
listdir 同时返回文件和文件夹,并不指出哪个是文件,哪个是文件夹。
|

|
你可以使用过滤列表和 os.path 模块的 isfile 函数,从文件夹中将文件分离出来。isfile 接收一个路径名,如果路径表示一个文件,则返回 1,否则为 0。在这里,我们使用 os.path.join 来确保得到一个全路径名,但 isfile 对部分路径 (相对于当前目录) 也是有效的。你可以使用 os.getcwd() 来得到当前目录。
|

|
os.path 还有一个 isdir 函数,当路径表示一个目录,则返回 1,否则为 0。你可以使用它来得到一个目录下的子目录列表。
|
例 6.19. 在 fileinfo.py 中列出目录
def listDirectory(directory, fileExtList):
"get list of file info objects for files of particular extensions"
fileList = [os.path.normcase(f)
for f in os.listdir(directory)] 
 fileList = [os.path.join(directory, f)
for f in fileList
if os.path.splitext(f)[1] in fileExtList]
fileList = [os.path.join(directory, f)
for f in fileList
if os.path.splitext(f)[1] in fileExtList] 


|
os.listdir(directory) 返回在 directory 中所有文件和文件夹的一个 list。
|
|
使用 f 对 list 进行遍历,我们使用 os.path.normcase(f) 根据操作系统的缺省值对大小写进行标准化处理。normcase 是一个有用的函数,用于对大小写不敏感操作系统的一个补充。这种操作系统认为 mahadeva.mp3 和 mahadeva.MP3 是同一个文件名。例如,在 Windows 和 Mac OS 下,normcase 将把整个文件名转换为小写字母;而在 UNIX 兼容的系统下,它将返回未作修改的文件名。
|

|
再次用 f 对标准化后的 list 进行遍历,我们使用 os.path.splitext(f) 将每个文件名分割为名字和扩展名。
|

|
对每个文件,我们查看扩展名是否在我们关心的文件扩展名 list 中 (fileExtList,被传递给 listDirectory 函数)。
|

|
对每个我们所关心的文件,我们使用 os.path.join(directory, f) 来构造这个文件的全路径名,接着返回这个全路径名的 list。
|
例 6.20. 使用 glob 列出目录
>>> os.listdir("c:\\music\\_singles\\")  ['a_time_long_forgotten_con.mp3', 'hellraiser.mp3',
'kairo.mp3', 'long_way_home1.mp3', 'sidewinder.mp3',
'spinning.mp3']
>>> import glob
>>> glob.glob('c:\\music\\_singles\\*.mp3')
['a_time_long_forgotten_con.mp3', 'hellraiser.mp3',
'kairo.mp3', 'long_way_home1.mp3', 'sidewinder.mp3',
'spinning.mp3']
>>> import glob
>>> glob.glob('c:\\music\\_singles\\*.mp3')  ['c:\\music\\_singles\\a_time_long_forgotten_con.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\hellraiser.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\kairo.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\long_way_home1.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\sidewinder.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\spinning.mp3']
>>> glob.glob('c:\\music\\_singles\\s*.mp3')
['c:\\music\\_singles\\a_time_long_forgotten_con.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\hellraiser.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\kairo.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\long_way_home1.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\sidewinder.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\spinning.mp3']
>>> glob.glob('c:\\music\\_singles\\s*.mp3')  ['c:\\music\\_singles\\sidewinder.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\spinning.mp3']
>>> glob.glob('c:\\music\\*\\*.mp3')
['c:\\music\\_singles\\sidewinder.mp3',
'c:\\music\\_singles\\spinning.mp3']
>>> glob.glob('c:\\music\\*\\*.mp3') 
|
正如你前面看到的,os.listdir 简单地取一个目录路径,返回目录中的所有文件和子目录。
|
|
glob 模块,另一方面,接受一个通配符并且返回文件的或目录的完整路径与之匹配。这个通配符是一个目录路径加上“*.mp3”,它将匹配所有的 .mp3 文件。注意返回列表的每一个元素已经包含了文件的完整路径。
|

|
如果你要查找指定目录中所有以“s”开头并以“.mp3”结尾的文件,也可以这么做。 |

|
现在考查这种情况:你有一个 music 目录,它包含几个子目录,子目录中包含一些 .mp3 文件。使用两个通配符,仅仅调用 glob 一次就可以立刻获得所有这些文件的一个 list。一个通配符是 "*.mp3" (用于匹配 .mp3 文件),另一个通配符是子目录名本身,用于匹配 c:\music 中的所有子目录。这看上去很简单,但它蕴含了强大的功能。
|
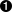
'c:\\music\\ap\\mahadeva.mp3' >>> os.path.join("c:\\music\\ap", "mahadeva.mp3")
'c:\\music\\ap\\mahadeva.mp3' >>> os.path.expanduser("~")
'c:\\Documents and Settings\\mpilgrim\\My Documents' >>> os.path.join(os.path.expanduser("~"), "Python")
'c:\\Documents and Settings\\mpilgrim\\My Documents\\Python'
('c:\\music\\ap', 'mahadeva.mp3') >>> (filepath, filename) = os.path.split("c:\\music\\ap\\mahadeva.mp3")
>>> filepath
'c:\\music\\ap' >>> filename
'mahadeva.mp3' >>> (shortname, extension) = os.path.splitext(filename)
>>> shortname 'mahadeva' >>> extension '.mp3'
['a_time_long_forgotten_con.mp3', 'hellraiser.mp3', 'kairo.mp3', 'long_way_home1.mp3', 'sidewinder.mp3', 'spinning.mp3'] >>> dirname = "c:\\" >>> os.listdir(dirname)
['AUTOEXEC.BAT', 'boot.ini', 'CONFIG.SYS', 'cygwin', 'docbook', 'Documents and Settings', 'Incoming', 'Inetpub', 'IO.SYS', 'MSDOS.SYS', 'Music', 'NTDETECT.COM', 'ntldr', 'pagefile.sys', 'Program Files', 'Python20', 'RECYCLER', 'System Volume Information', 'TEMP', 'WINNT'] >>> [f for f in os.listdir(dirname) ... if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(dirname, f))]
['AUTOEXEC.BAT', 'boot.ini', 'CONFIG.SYS', 'IO.SYS', 'MSDOS.SYS', 'NTDETECT.COM', 'ntldr', 'pagefile.sys'] >>> [f for f in os.listdir(dirname) ... if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(dirname, f))]
['cygwin', 'docbook', 'Documents and Settings', 'Incoming', 'Inetpub', 'Music', 'Program Files', 'Python20', 'RECYCLER', 'System Volume Information', 'TEMP', 'WINNT']
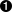
fileList = [os.path.join(directory, f) for f in fileList if os.path.splitext(f)[1] in fileExtList]


['a_time_long_forgotten_con.mp3', 'hellraiser.mp3', 'kairo.mp3', 'long_way_home1.mp3', 'sidewinder.mp3', 'spinning.mp3'] >>> import glob >>> glob.glob('c:\\music\\_singles\\*.mp3')
['c:\\music\\_singles\\a_time_long_forgotten_con.mp3', 'c:\\music\\_singles\\hellraiser.mp3', 'c:\\music\\_singles\\kairo.mp3', 'c:\\music\\_singles\\long_way_home1.mp3', 'c:\\music\\_singles\\sidewinder.mp3', 'c:\\music\\_singles\\spinning.mp3'] >>> glob.glob('c:\\music\\_singles\\s*.mp3')
['c:\\music\\_singles\\sidewinder.mp3', 'c:\\music\\_singles\\spinning.mp3'] >>> glob.glob('c:\\music\\*\\*.mp3')
